Income Tax Audit easy guide F.Y. 2021-22
Income Tax Audit is governed by Section 44AB of the Income Tax Act, 1962. Finish Income Tax Audit in an hour by reading this easy guide. This article is a detail guide on on whom and when Income Tax Audit is applicable, key issues faced in Income Tax Audit and finish Income Tax Audit in an hour by following steps.
Also refer article >> https://www.taxledgeradvisor.com/is-tax-audit-compulsory-in-case-of-losses/ for special case wherein business has incurred loss, then will tax audit will be compulsory for such business?
First Step before Income Tax Audit is started is to check whether Tax Audit is applicable on assessee and under which section of 44AB same is applicable.
Income Tax Audit applicability calculator F.Y. 2021-22 and A.Y. 2022-23
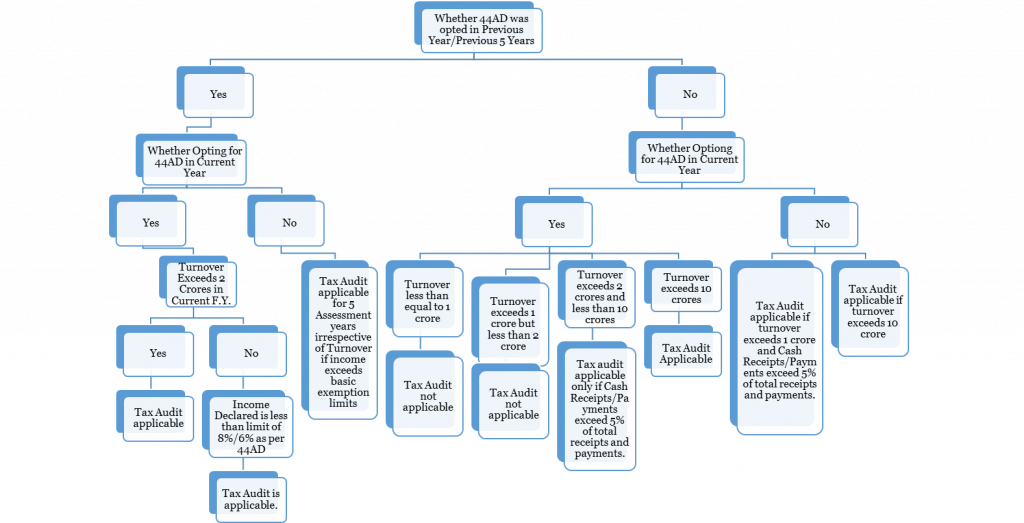
On whom Tax Audit is applicable?
Every person as defined in Section 2(31) of the Income Tax Act being Individual, Hindu Undivided Families [HUFs], Association of Persons [AOPs], Body of individuals [BOIs], Firms, LLPs, Companies, Local authority and any artificial juridical person.
When is Tax Audit applicable?
- Person carrying on business if total sales/turnover/gross receipts exceeds one crore.
- However, if Cash Receipts and Cash Payments does not exceed 5% of total cash receipts and payments then tax audit is applicable only if the limit of total sales/turnover/gross receipts exceeds 10 crores.
- Person carrying on profession if gross receipts in profession exceeds 50 lacs,
- Person carrying on business who has declared Lower profits from as would have been deemed under section 44AE, 44BB or 44BBB
- Person carrying on profession who has declared Lower profits from as would have been deemed under section 44ADA and income so declared exceeds the maximum exemption limit chargeable to tax (i.e., 2.5 lacs)
- Person carrying on business and on whom provision of Section 44AD (4) are applicable and income exceeds the maximum exemption limit chargeable to tax (i.e., 2.5 lacs)
- Provided if income declared as per section 44AD (1), then tax audit is applicable only if total sales/turnover/gross receipts from business exceeds 2 crores.
This section not applicable on person who derives income as per Section 44B (Special provision for computing profits and gains of the business of operation of aircraft in the case of non-residents) & 44BBA (Amount received in India or deemed to be received in India by or on behalf of the taxpayer on account of carriage of passenger, livestock, mail or goods from any place outside India.)
Relevant extracts of Section 44AD
44AD (1) – Eligible assessee carrying on eligible business can declare a sum equal to 8% of the total turnover or gross receipts or such higher sum earned, shall be deemed to profits and gains of business chargeable to tax.
44AD (4) Eligible assessee who declares income as per Sub Section 1 above then he has to declare profits for five years in accordance with sub section 1. However, if he opts out in any of the year then he would not be eligible to opt for Sec 44AD (1) for 5 years from the year he opted out
Income Tax Audit Form applicable
Income Tax Audit Form prescribed is Form 3CA – 3CD for taxpayers carrying on a business or profession and who is already mandated to get his accounts audited under any other law. Eg: Companies.
Income Tax Audit Form prescribed is Form 3CB – 3CD for all the other taxpayers. Eg: Individual or HUF.
For Form 3CD format F.Y. 2021-22 refer >> https://www.incometaxindia.gov.in/forms/income-tax%20rules/103120000000007767.pdf
Due Date of Income Tax Audit
Due date of Income Tax Audit is 30 September from the end of Financial Year.
Due of F.Y. 2021-22 Income Tax Audit is 30-Sept-2022.
Finish Income Tax Audit in an hour by following steps
- Use filters on Day Book and extract all transactions having amount exceeding INR 10,000 and with ledger cash. This will help to quickly address all of the cash points in Tax Audit Report.
- Extract the Fixed Asset Register and make a excel working for Depreciation as per Income Tax Act.
- Identify related parties and check loans and advances received or repayment or any transactions with related parties for reporting purpose in tax audit report.
- Perform Bank Reconciliation, verify closing balances and on sampling basis check transactions as per bank statement and transactions recorded in books.
- Obtain Creditor and Debtor Confirmation statements.
- Verify GST Turnover as per GST Portal & as per books.
- Verify Sales and Purchases vouchers on sampling basis.
- Verify Expenses to check TDS applicability and same was deducted & deposited and return was filed.
- Verify no personal, advertisement or capital expenditure were charged to Profit & Loss Account.
- Disallow all the payments as per section 43B paid till return filing date.
Key issues faced in Income Tax Audit
- Reporting of quantitative details of stock i.e. opening, closing, purchases, sales or consumption.
- Reporting of Break-up of total expenditure of entities registered or not registered under the GST as most of the software’s available in India does not provide information in this format.
- Identification of Related parties of assessee.
Income Tax Audit requirement in Udaipur and Rajasthan
For Income Tax Audit requirement in Udaipur and Rajasthan, reach our professionals at Tax Ledger Advisor.


